Placing a new security on the securities market is a complex process that involves several key steps.
Working through a refinance of the CFG 2021-1 Securitization (referred to as SEC in this blog at times) allowed me to work closely with these key steps and this blog post will provide an overview of these steps and highlight the importance of careful planning and execution.
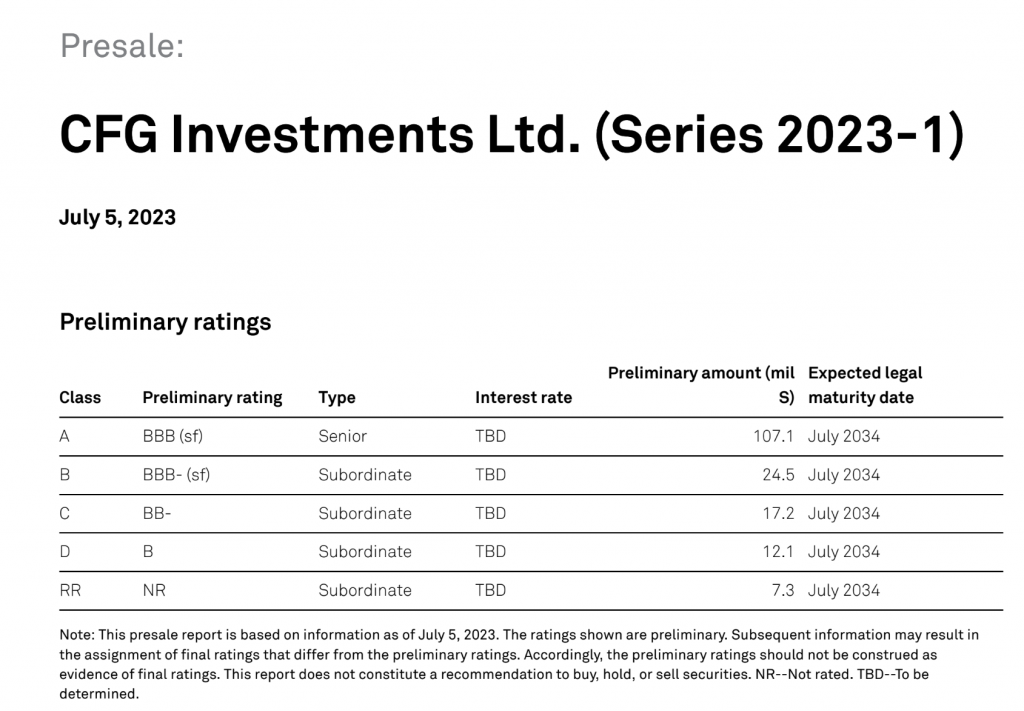
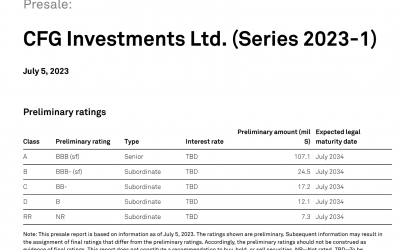
S&P Global Rating:
Step 1: Identifying the Security
The first step in placing a new security on the securities market is to identify the type of security that will be offered. This could be stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments. It is crucial to understand the characteristics and risks associated with the security before proceeding to the next steps.
For the 2023-1 CFG SEC the underlying collateral were unsecured personal loan receivables originated in four different jurisdictions in the Caribbean. A majority of the underlying collateral was being pledged to the new SEC from the closing 2021-1 SEC that was being refinanced through the new SEC.
Having the underlying collateral that would back the SEC organized and detailed was extremally important to ensure the closing SEC and new SEC were properly supported. A collateral waterfall was created that would detail the current position (where collateral was pledged, i.e. still on Balance Sheet, existing SEC, or another finance facility), UPB (Unpaid Principal Balance), and other key collateral details.
144A Market Details
The CFG SEC was placed on the 144a market, as the unique structure and underlying collateral of this SEC makes this investment opportunity best suited for qualified institutional buyers (QIB).
Rule 144A, established by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), provides a safe harbor exemption for the resale of certain privately placed securities to qualified institutional buyers (QIBs). This rule allows for the efficient trading of restricted securities, which are typically securities that cannot be publicly traded due to certain restrictions or limitations.
The impact of Rule 144A is significant as it expands the potential investor base for securities offerings. By allowing qualified institutional buyers to participate in private placements, issuers have access to a larger pool of potential investors, which can enhance liquidity and potentially improve pricing for the securities being offered. Additionally, Rule 144A provides flexibility and efficiency in the trading of restricted securities, as it exempts these transactions from the registration requirements of the Securities Act of 1933.
It is important for issuers and professionals involved in the placement of new securities to understand and comply with the requirements of Rule 144A. By doing so, they can tap into the benefits provided by this rule and navigate the securities market more effectively.
Step 2: Preparing the Documentation
Once the security is identified, the next step is to prepare the necessary documentation. This includes drafting a prospectus, which provides detailed information about the security, its terms, and the risks involved. It is important to ensure that the prospectus complies with all applicable regulations and provides accurate and transparent information to potential investors.
This step ties in with Step 3, and the idea is to continue reviewing and elaborating on documentation and details. At this stage it is best to start to establish a timeline to ensure items are delivered on schedule and team members are head accountable. Here a Gannt chart was established along with a document list to ensure that everything was accounted for and target deadlines could be met.
Step 3: Engaging with Professionals
To successfully place a new security on the securities market, it is advisable to engage with professionals such as investment bankers, lawyers, and auditors. These professionals can provide valuable expertise and guidance throughout the process. They can assist with pricing the security, structuring the offering, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
The structuring advisors for the 2023-1 SEC was Guggenheim, being a key partner in organizing the SEC and getting it to market. Since this wasn’t the first SEC CFG has brought to market with Guggenheim, the turn around time on planning and materials was quicker. The right professionals can make or break a deal, so establishing key parties is very important to get situated.
More details on ABS (Asset-Backed Securities) like CFG SEC 2023-1 from Guggenheim.
Weil was part of the legal counsel and key for ensuring legal documentation was adequately set.
Step 4: Marketing and Investor Outreach
Effective marketing and investor outreach are crucial to attract potential investors to the new security offering. This may involve conducting roadshows, where the company or issuer presents the investment opportunity to potential investors. It is important to highlight the unique features and benefits of the security and address any investor concerns or questions.
The type of investors is another thing to look at as well, where the type of investors can dictate sentiment to the overall market. Larger more “institutional” investors signals to the market that a security is a “safer” investment, which can lead to a better overall sentiment which can drive to more interest from investors and improved pricing.
Step 5: Pricing and Allocation
Once there is sufficient investor interest, the next step is to determine the pricing and allocation of the new security. This involves working closely with underwriters and investment banks to set the initial offering price and allocate shares or bonds to investors. Proper pricing and allocation strategies are essential to ensure a successful offering.
Benchmarks & Pricing
In the context of pricing a security, a benchmark is a standard or reference point used to determine the appropriate pricing level for the security. It provides a point of comparison for investors and market participants to evaluate the value of the security being offered.
A benchmark can take various forms depending on the type of security and the market in which it is being priced. For example, in the case of bonds, a common benchmark is the yield on comparable government bonds or other similar securities with similar credit ratings and maturities. This allows investors to assess the relative attractiveness of the security’s yield in comparison to other available investment options.
The benchmark serves as a guide for pricing the security by establishing a reference point against which the security’s risk and return characteristics can be evaluated. It helps market participants gauge the fair value of the security and make informed investment decisions.
When pricing a security, market participants will typically consider factors such as the credit quality of the issuer, prevailing market interest rates, market demand for similar securities, and the overall economic environment. By comparing these factors to the benchmark, they can determine an appropriate pricing level that reflects the perceived risk and potential return of the security.
It is important to note that benchmarks are not fixed or static. They can change over time as market conditions and investor preferences evolve. Therefore, market participants need to continuously monitor and reassess the benchmark to ensure that the pricing of the security remains relevant and competitive.
Overall, benchmarks play a crucial role in pricing securities as they provide a standardized reference point for assessing the value and attractiveness of the security in the market. They help align pricing expectations and facilitate efficient price discovery, ultimately contributing to the smooth functioning of the securities market.
Pricing a Security: Understanding the Spread
Spread is another component that is key when pricing a security, and the one that issuers have the most “control” over.
When a new security is issued, the spread can refer to the difference between the yield of the newly issued security and the yield of a benchmark or reference security, such as a government bond. This spread compensates the investor for the additional risk they take on when investing in the new security, compared to the benchmark.
The size of the spread can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the creditworthiness of the issuer, the length of time until the security matures, and the liquidity of the security. For example, securities issued by a company with a high credit rating will typically have a smaller spread compared to securities issued by a company with a lower credit rating.
Furthermore, the spread can also be influenced by overall market conditions. In times of economic uncertainty, investors may demand a higher spread to compensate for the increased risk. Conversely, during periods of economic stability, the spread may decrease as investors are willing to accept lower returns for less risk.
Determining the appropriate spread is a crucial part of the securities pricing process. It requires a deep understanding of the market, the characteristics of the security, and the risk tolerance of potential investors. By accurately pricing the spread, issuers can attract the right investors, meet their funding needs, and ensure the successful placement of the new security in the market.
Step 6: Listing and Trading
The final step in placing a new security on the securities market is listing and trading. For securities listed on the 144a market, this process may look a little different than traditional public markets.
Listing and trading a security on the 144A market involves a careful consideration of the unique characteristics of this marketplace. It is important to work with experienced professionals who understand the intricacies of the 144A market to ensure a smooth and successful listing and trading process.
With the investors in place, the SEC is ready to go live with notes being issued to the relevant investors.
Placing a new security on the securities market requires careful planning, documentation, engagement with professionals, effective marketing, and strategic pricing. By following these steps and seeking expert advice, issuers can navigate the complexities of the securities market and successfully raise capital.
Remember, the process may vary depending on the jurisdiction and type of security being offered. It is important to consult with legal and financial professionals to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations and best practices.
This was a great experience for me, where I was able to see the process start to finish with CFG, and working with many great relative experts in the field. We were able to finish the issuance providing a great offering; and I’m looking forward to the next deal.